9.14 Gas Metal Arc Spot Welding
A gas metal arc welding power source and arc welding gun can be used to produce a weld in one small spot, called a spot weld. Metals commonly welded with the gas metal arc spot welding process are low-carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, copper-based metals, and magnesium. Although, gas metal arc spot welding is generally done on metals under 1/16″ (1.6mm) thick, metals up to 3/16″ (5mm) thick can be welded.
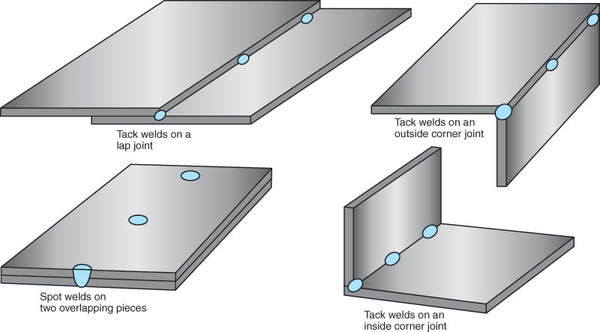
Small tack welds are made on lap and corner joints using spot welding techniques. See Figure 9-64. A spot weld is a weld made at a single point on overlapping pieces.
Small tack welds are made on lap and corner joints using spot welding techniques. See Figure 9-64. A spot weld is a weld made at a single point on overlapping pieces.
A manually controlled spot weld is made by positioning the welding wire above the location where the spot or tack is to be made. The trigger on the welding gun is pulled. No movement of the gun takes place. After the weld pool is formed, the trigger is released. The welder sets the voltage and wire feed speed as is done when running a weld bead. The weld time is controlled by the welder. This technique is used to tack parts together. It can also be used to weld through a thin metal sheet to join it to a piece of metal beneath the thin top sheet.
The weld time can be controlled by the welding power source if it is equipped with timer controls. The welder sets the desired weld time on the power supply. When the gun trigger is pressed, the arc takes place for a set and controlled time. This way every GMAW spot weld will be the same time. A completed GMAW spot weld is shown in Figure 9-65.
The weld time can be controlled by the welding power source if it is equipped with timer controls. The welder sets the desired weld time on the power supply. When the gun trigger is pressed, the arc takes place for a set and controlled time. This way every GMAW spot weld will be the same time. A completed GMAW spot weld is shown in Figure 9-65.
Gas metal arc spot welds on thin metals can be made in any position. As the metal thickness increases, GMA spot welding is limited to the flat welding position. Weld quality and uniformity is not as good as that possible with resistance spot welding. The big advantage of GMA spot welding over resistance spot welding is that access to only one side of the parts is required.