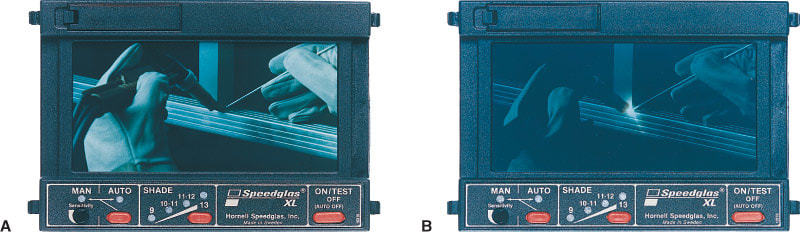
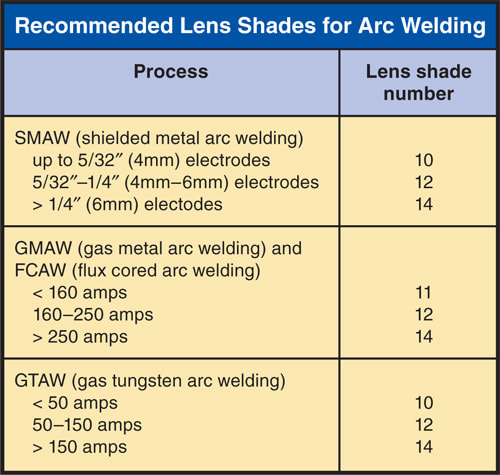
7.15 Filter Lenses for Use When Gas-Shielded Arc Welding
Because of the clearer atmosphere around the arc, the operator must use arc welding lenses with a darker shade to reduce eye fatigue and possible eye damage. Most helmets for gas arc welding use a clear cover lens and a filter lens. Sometimes a clear cover lens is used on the inside of the helmet, as well. It is very important that all these lenses be clean. Figure 7-64 shows a helmet with a lens that automatically darkens when an arc is struck. Figure 7-65 shows the effect of an autodarkening change lens. Figure 7-66 lists recommended shade numbers for gas tungsten, gas metal, and flux cored arc welding.
7.16 Protective Clothing
Accessories of leather are recommended. Additional options to wear include clothing made of heavy wool or cotton. Cotton may be treated to reduce its ability to burn. Always wear dark clothing to reduce reflection of light behind the helmet. Clothing worn while welding should have no cuffs or open pockets, since these can collect sparks.
Leather gloves should be worn. See Chapter 1 for additional information on clothing recommended for arc welding.
7.17 Safety Review
When using gas tungsten, gas metal, or flux cored arc welding equipment, follow all the safety precautions normally used with arc welding equipment. These include the following:
Because of the clearer atmosphere around the arc, the operator must use arc welding lenses with a darker shade to reduce eye fatigue and possible eye damage. Most helmets for gas arc welding use a clear cover lens and a filter lens. Sometimes a clear cover lens is used on the inside of the helmet, as well. It is very important that all these lenses be clean. Figure 7-64 shows a helmet with a lens that automatically darkens when an arc is struck. Figure 7-65 shows the effect of an autodarkening change lens. Figure 7-66 lists recommended shade numbers for gas tungsten, gas metal, and flux cored arc welding.
7.16 Protective Clothing
Accessories of leather are recommended. Additional options to wear include clothing made of heavy wool or cotton. Cotton may be treated to reduce its ability to burn. Always wear dark clothing to reduce reflection of light behind the helmet. Clothing worn while welding should have no cuffs or open pockets, since these can collect sparks.
Leather gloves should be worn. See Chapter 1 for additional information on clothing recommended for arc welding.
7.17 Safety Review
When using gas tungsten, gas metal, or flux cored arc welding equipment, follow all the safety precautions normally used with arc welding equipment. These include the following:
- Electrical connection leads should be in good condition and tight. They should be protected from accidental damage from shop traffic.
- Prevent fumes and contaminated air from reaching the welder's face during welding. Adequate ventilation and filtration equipment must be used. In some welding conditions, it is necessary to use a purified air breathing apparatus.
- Proper clothing should be worn to prevent burns from hot metal and ultraviolet and infrared rays.
- Flammable materials should not be carried in pockets. Pockets should be closed and cuffs rolled down to prevent hot metal from going into them.
- Always wear a welding helmet with the proper number filtering lens for the type of welding being done.
- Shielding curtains should be placed around all jobs so that workers in the area are protected from arc flashes.
|
|